Electricity retailers sometimes give the choice of paying a flat rate for electricity, or so called Time of Use (ToU) rate. Time of use pricing usually has peak, off-peak and shoulder prices. This can also vary by time of year and also weekend or weekday.
For the consumer, Time of Use pricing may be beneficial if consumption can be shifted to off-peak hours, but this is potentially offset by more expensive rates during peak times.
Assuming a retailer gives the ability to choose – which one is cheaper?
Solution
This web calculator gives the ability to simulate costs based on historical meter data usage and configurable pricing and peak/off-peak definition:
https://niftimus.github.io/EnergyAnalyser/
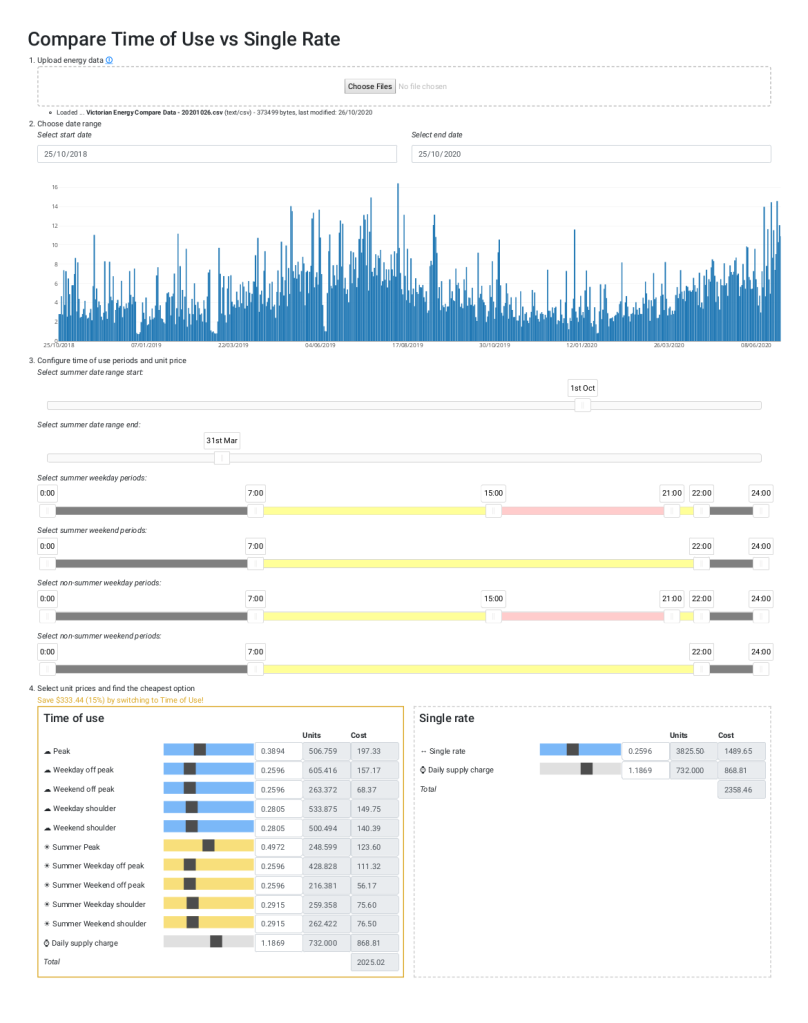
Note: Beta only. Default prices may be different depending on the retailer or electricity plan, but the sliders allow adjustment to configure unit prices to match any real plan for comparison.
Features
- Calculate costs, potential savings and get a recommendation:

- Fully client-side, JavaScript and HTML – no server upload required
- Ability to drag-and-drop upload a Victorian Energy Compare formatted CSV:

- Focus on a particular date range within the uploaded meter data:

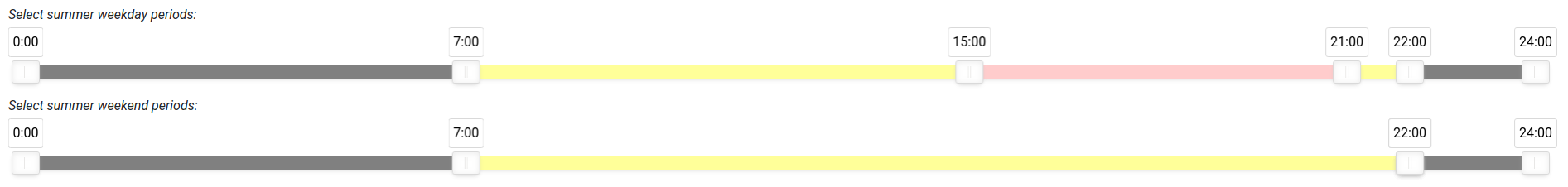
- Ability to configure time of use definitions (i.e. peak, off-peak and shoulder times):
Potential future improvements
The following future improvements could make the solution more useful:
- Cope with different data formats (different States’ data)
- Ability to compare two (or n) different plans
- Automatic comparison of available plans from multiple retailers (pulling prices automatically)
- Inclusion of solar feed-in tariff as a comparison point
- Provide recommendations for changing energy usage behaviour
- Simulate the impact of having a home battery
